Week 1 - Defining Health Systems Science and Health
Session 1 – What is Health Systems Science?
- Spark Questions
- Session summary and reflection
- Learning Outcome
- Concluding Questions: Defining Health & Health Systems Sciences
Spark Questions
As a health science student, why do you think it is important to study health science system?
Health Science system provides a broad understanding of the frameworks of health care. There always is a need for structure or a system for people to follow or there will be chaos. Everyone in health science is brilliant but too many brilliant ideas without structure is useless.
If someone comes up with the next best drug that will cure cancer and there is no pharmacist to make or distribute. The drug becomes pointless. If there is no oncologist that can diagnose cancer there will be no point of the pharmacist or the researcher who came up with the drug. The correct patients will most likely not get the correct drug. If there is no primary physician that would refer the patient to the oncologist the entire train of health care providers is pointless.
Everyone needs to follow a system so that resources are not wasted. There is no one that can specialise in everything and even if 1 person could, it would take too long and humans, especially human brains, have an expiry date. Following a chain of specialties not only provides structure but also increases efficiency in health care so that a patient can receive the best possible health care. In order to provide this understanding of these systems so that it can be implemented later, it is crucial for health science students to study Health science systems
Session summary and reflection
- HSS1 is split into 3 core disciplines: (slide 3)
- Health System Science: Structure of systems
- Public Health: Actual health of population and need for systems
- Bioethics and health laws: Consequences of actions and how law helps protect patients from these consequences.
- Two important pillars of health science are Basic Sciences and Clinical Science. The third pillar of health system sciences is often overlooked but is crucial. Health care professionals do not work in isolation. If they did there would be a significant decrease in efficiency. This is why health science systems is important. It allows for structure to allow health care professionals to work together bettering the overall health care for patients. (slide 5)
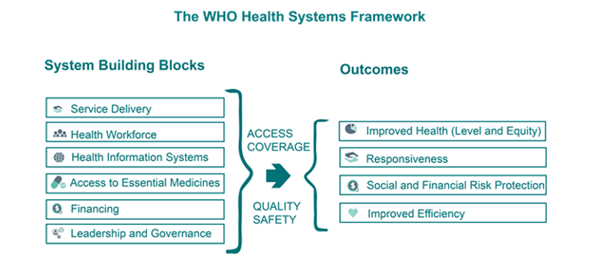
- The 3 main goals with HSS: (slide 9)
- Improving patients’ experiences of health care (i.e. Better Care)
- Improving the health of the population (i.e. Improved Health)
- Decreasing the cost of health care (i.e. Lower Costs)
- System thinking involves 3 criteria’s: (https://youtu.be/HzT1-BZIJQA?feature=shared)
- Interrelationships – Looking at patterns between businesses and individuals to connect every discipline
- Perspectives – Looking at how other perceive things and how the feel. Focusing on the quality of care instead of quantity.
- Boundaries – Finding obstructions to new innovations and solving the issues.
- I previously Considered HSS as common sense and unnecessary but after this session I understand its complexities and necessity. Without HSS the entire health care system will fall apart.
Learning outcome - What is Health Systems Science?
- Locate HSS within the health sciences more broadly.
- HSS provides a structure and joins the two important pillars of health science, Basic Sciences and Clinical Science
- Explain the difference and interrelatedness between core, cross-cutting, and complementary content.
- Core content – Different parts of health systems
- Cross-cutting content – The skills we will learn while learning core concepts
- Complementary content – history and ethics which provides more context to the syllabus
- Locate and discuss the role and interrelatedness of public health and bioethics, human rights, and health law within the HSS as a discipline.
- Health System Science is the structure of systems
- Public Health is the actual health of population and need for systems
- Bioethics and health laws is the consequences of actions and how law helps protect patients from these consequences.
- These 3 disciplines are interconnected and will fail without the other.
Conclusion questions: Defining Health & Health Systems Sciences
- What do you think Health Systems Sciences is as a discipline of study?
- Health System Sciences is a vital part of health care. Without HSS all other disciplines collapse. HSS provides a structure that is needed for efficiency and the best health care we can provide.
- What are the different core elements that makeup Health Systems Science?
- Health System Science: Structure of systems
- Public Health: Actual health of population and need for systems
- Bioethics and health laws: Consequences of actions and how law helps protect patients from these consequences.
- What does being healthy mean to you?
- Health is a state of physical, mental, and social well-being. It is the ability to manage and adapt in order to be content with one’s state of physical, mental, and social well-being. It is not the absence of diseases nor infirmity but how the individual is with the disease or infirmity
- If health is not just about physical well-being, what other aspects do you think should be considered when forming a definition for health?
- Mental wellbeing
- Ability to adapt to different health challenges
- Do you think that a universal definition of health is possible? Why or why not?
- No because health is in a constant state of change but we could get close
- What do you think it means when we say that health is socially constructed?
- Being healthy is biased to how you feel. The majority of people do not suffer from HIV or AID, so they do not have to keep taking medication to be healthy. The many could be biased saying taking pills is unhealthy but that is not true. The majority may feel a certain way about health because of their experiences without looking at the facts.